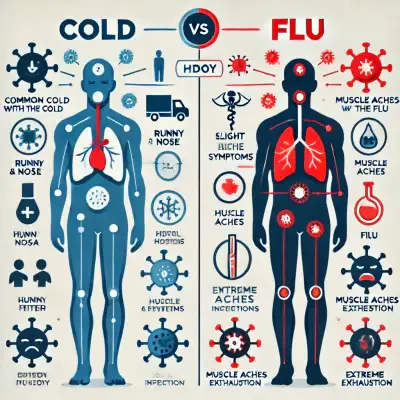
Cold and flu season can be confusing, as both illnesses share similar symptoms. However, they are caused by different viruses and vary in severity. While the common cold is mild and resolves on its own, influenza (flu) can lead to severe complications such as pneumonia and hospitalization. Understanding the key differences, symptoms, and prevention strategies can help you stay healthy during flu season.
Cold vs Flu: Key Differences
Understanding the key differences between a cold and the flu is crucial, as it helps determine the appropriate treatment and when to seek medical attention. While both illnesses affect the respiratory system, their severity, duration, and potential complications vary significantly.
| Feature | Common Cold | Influenza (Flu) |
|---|---|---|
| Cause | Rhinovirus, adenovirus | Influenza A or B virus |
| Onset | Gradual | Sudden and severe |
| Fever | Rare or low-grade | High fever (100.4°F–104°F) |
| Cough | Mild | Severe, persistent |
| Muscle Pain | Rare | Severe body aches |
| Nasal Congestion | Common | Less common |
| Headache | Rare | Common and intense |
| Fatigue | Mild | Severe exhaustion |
| Recovery Time | 7–10 days | 1–2 weeks or longer |
| Complications | Rare | Pneumonia, myocarditis |
Quick Tip: If you have sudden high fever, chills, and body aches, it’s likely the flu rather than a cold. Seek medical attention early!
Cold & Flu Causes: How Do You Get Sick?
Both colds and flu are highly contagious and spread through:
Airborne droplets from coughing, sneezing, or talking
Touching contaminated surfaces and then touching your face
Close contact with an infected person
Flu viruses can survive on surfaces for hours! Frequent handwashing is crucial for prevention.
Common Cold Symptoms & Treatment
Colds primarily affect the nose and throat and typically present with:
Runny or stuffy nose
Mild sore throat
Occasional cough
Mild fatigue
Treatment:
Stay hydrated (water, herbal teas, broth)
Rest to support the immune system
Steam inhalation to relieve congestion
Over-the-counter medication for symptom relief
Antibiotics do NOT work against colds because they are viral infections.
Flu Symptoms: Why It’s More Dangerous
Unlike colds, the flu affects the entire body and can cause severe symptoms:
High fever (100.4°F–104°F)
Severe muscle aches and chills
Extreme fatigue (can last for weeks)
Persistent dry cough
Loss of appetite
When to Seek Medical Help?
Flu can become life-threatening, especially for:
Elderly individuals (65+)
Pregnant women
People with chronic conditions (asthma, diabetes)
Infants and young children
If you experience difficulty breathing, chest pain, persistent vomiting, or worsening fever, seek immediate medical attention.
Flu Without a Fever? It Happens!
Many people associate the flu with a high fever, but some cases occur without fever, making diagnosis more challenging. This can lead to misdiagnosis or delayed treatment, increasing the risk of complications.
Why Can Flu Occur Without a Fever?
Elderly individuals & immunocompromised patients may not mount a strong fever response.
Certain flu strains trigger more respiratory symptoms rather than systemic fever.
Healthy adults with robust immune systems may suppress fever but still experience severe fatigue, body aches, and cough.
Why Early Diagnosis Matters
Even without a fever, flu can still be highly contagious and lead to complications such as pneumonia. If you experience persistent fatigue, a dry cough, body aches, and extreme exhaustion, consult a healthcare provider. Early detection can help reduce the severity and duration of symptoms. Some flu cases occur without fever, especially in:
Elderly individuals & immunocompromised patients
People with specific flu strains causing more respiratory symptoms
Healthy adults with strong immune responses suppressing fever
If you have persistent fatigue, cough, and body aches without fever, flu is still possible.
Flu Complications: How Dangerous Can It Get?
If untreated, the flu can lead to:
Pneumonia
Myocarditis (heart inflammation)
Brain inflammation (encephalitis)
Respiratory failure requiring hospitalization
In the U.S., flu complications cause tens of thousands of hospitalizations every year.
Best Ways to Prevent Cold & Flu
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is key to preventing both colds and the flu. Strengthening your immune system and adopting good hygiene practices can significantly reduce your risk of infection.
1. Get a Flu Shot Every Year
Reduces hospitalization risk by up to 60%
Helps protect high-risk groups
Milder symptoms if infected after vaccination
2. Wash Hands Frequently
Scrub for at least 20 seconds
Use alcohol-based sanitizers when needed
3. Boost Your Immune System
Eat a vitamin C, D, and zinc-rich diet
Get 7–9 hours of sleep
Exercise regularly
4. Avoid Crowded Places
Wear a mask in high-risk areas
Minimize exposure to infected individuals
5. Stay Home If You’re Sick
Rest prevents spreading the virus
Stay hydrated and monitor symptoms
Tip: Disinfect commonly touched surfaces like doorknobs and phones to reduce transmission risk.
Final Thoughts: Prevention is the Best Cure!
Colds are mild, while flu can be severe and even fatal.
The flu shot is the most effective prevention method.
Early treatment reduces complications.
Want to Stay Flu-Free This Winter? Get vaccinated and follow these prevention tips!
Schedule your flu shot today!
Stay healthy and safe! 😊
Colds are mild, while flu can be severe and even fatal.
The flu shot is the most effective prevention method.
Early treatment reduces complications.
Want to Stay Flu-Free This Winter? Get vaccinated and follow these prevention tips!
Stay healthy and safe! 😊
Get More Insights: Economics, Certifications, Legal Updates, and Beyond!
Want to stay ahead of the curve with more in-depth information on economics, professional certifications, legal updates, and a variety of other topics? Leave your email in a private comment below! We'll be launching a newsletter soon to deliver exclusive content and updates directly to your inbox. Don't miss out on valuable insights beyond our regular blog posts!